ความรู้ทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับพลาสติกวิศวกรรม
General Information about ENGINEERING Plastics
พลาสติกคืออะไร?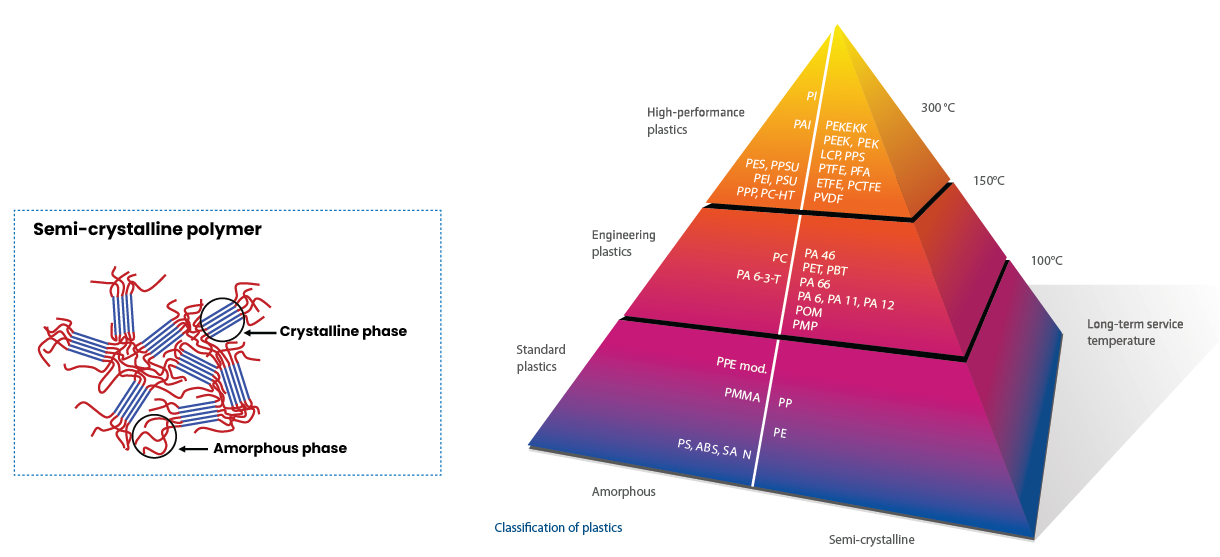
พลาสติกคือวัสดุพอลิเมอร์ที่สามารถขึ้นรูปเป็นผลิตภัณฑ์ได้หลากหลาย แบ่งออกเป็น 2 ประเภทหลัก:
- เทอร์โมพลาสติก – มีโครงสร้างทั้งที่เป็นระเบียบ (Crystalline phase) และไม่เป็นระเบียบ (Amorphous phase) สามารถหลอมแล้วขึ้นรูปใหม่ได้
- เทอร์โมเซต – มีโครงสร้างเชื่อมขวาง ถาวร แข็งแรง ทนความร้อน แต่ไม่สามารถหลอมใหม่ได้
พลาสติกวิศวกรรมคืออะไร?
พลาสติกวิศวกรรมคือพลาสติกสมรรถนะสูงในกลุ่มเทอร์โมพลาสติก โดดเด่นเรื่องความแข็งแรง ทนความร้อน ทนสารเคมี และเป็นฉนวนไฟฟ้า
คุณสมบัติหลักได้แก่:
- มีโครงสร้าง semi - Crystalline เช่น UHMW-PE
- มีโครงสร้างพันธะไฮโดรเจน เช่น ไนลอน และเคฟลาร์
- มีวงแหวนอะโรแมติกในสายโซ่ เช่น PEEK
ข้อดีเมื่อเทียบกับโลหะ
- -น้ำหนักเบา
- -ทนสารเคมีและไม่เป็นสนิม
- -เป็นฉนวนไฟฟ้าและความร้อน
- -ขึ้นรูปง่าย มีสีให้เลือก
- -ช่วยลดการใช้พลังงาน
What are Plastics?
Plastics are polymer materials that can be molded into various products. They are mainly categorized into two types:
- Thermoplastics – Contain both crystalline (ordered) and amorphous (random) phases. They can be remelted and reshaped.
- Thermosets – Permanently crosslinked structure. Strong and heat-resistant but cannot be remolded once set.
What are Engineering Plastics?
Engineering plastics are high-performance thermoplastics with excellent strength, heat resistance, chemical resistance, and electrical insulation.
Key properties include:
- Semi-crystalline structure, e.g., UHMW-PE
- Hydrogen-bonded networks, e.g., nylon and Kevlar
- Aromatic rings in the polymer backbone, e.g., PEEK
Advantages over Metals
- -Lightweight
- -Chemical and corrosion resistant
- -Good thermal and electrical insulation
- -Easy to mold and color
- -Energy-efficient in processing